For many people, constant ringing, buzzing, swooshing, or hissing sounds can be frustrating. For some of you, it can be a minor annoyance, but for others, it can disrupt concentration, sleep, and affect the overall health. Unfortunately, tinnitus cannot be cured; however, various tinnitus management techniques are available that can reduce tinnitus and offer relief. The use of hearing aids, mostly known for addressing hearing loss, is also a remedy as hearing aids help tinnitus by masking ringing and buzzing. This complete guide explains how hearing aids help tinnitus.
Does Tinnitus Cause Hearing Loss?
Tinnitus does not cause hearing loss, although your chances of having hearing loss are high if you have tinnitus. According to the Hearing Loss Association of America, 50 million Americans experience tinnitus, and 90% of them have hearing loss.
How Does Tinnitus Affect Your Hearing?
If you experience tinnitus, then the chance of hearing loss is high, as the parts of the inner ear responsible for hearing can be the likely cause of tinnitus.
The tiny hair cells in the cochlea are responsible for your hearing. They convert sound waves into electrical pulses that reach the brain through the auditory nerve. These pulses are interpreted by the brain as sounds.
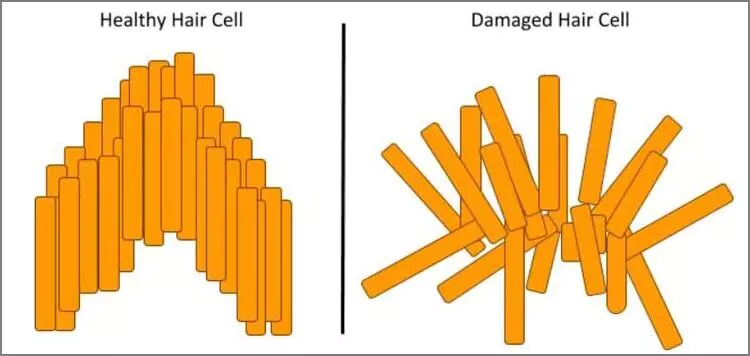
The delicate hair cells can get damaged due to exposure to loud sounds, infections, or old age. At times, the damaged hair cells behave erratically, sending confusing signals to the brain even if no sound is present. According to Byung In Han, Ho Won Lee and others from the Korean Neurological Association, in an article available in the Pubmed Central, the brain interprets these signals as ringing, buzzing, whooshing, or other tinnitus sounds.
Tinnitus is not solely an ear-related issue. Over time, the brain aggravates this issue as it amplifies these phantom sounds, making the tinnitus sound louder.
How Do Hearing Aids Help Tinnitus?
As 90% of the people experiencing tinnitus also suffer from hearing loss, the use of hearing aids helps tinnitus and also manage hearing loss. A study titled Hearing Aid Effectiveness on patients with chronic tinnitus and associated hearing loss published in 2022 concluded that hearing aids help tinnitus and is a valuable treatment strategy.
• Tinnitus Masking Hearing Aids
Most reputed brands offer hearing aids with tinnitus masking features. These hearing aids help tinnitus by producing a sound that masks or drowns the tinnitus sound. The in-built tinnitus masking generator produces white noise, special masking tones, or soft music.
If the tinnitus sounds you experience are high-pitched or in the high-frequency range, the chances are that your hearing loss is also in the same region. If your hearing loss is in one ear, the tinnitus will also be in the same ear.
You can switch between masking sounds and select the sound that offers maximum relief, as it will depend on the type and intensity of your tinnitus.
Bluetooth hearing aids can connect to your smartphone; in this case, you can download free and paid tinnitus masking apps available on iPhone App store and Android Play store. Pleasing sounds such as falling raindrops or gentle splashing waves can be downloaded and played through your hearing aids providing relief.
Free download of tinnitus masking sounds is available from the American Tinnitus Masking Sound Library.
• Auditory Stimulation
Hearing aids help tinnitus by providing increased auditory stimulation to the brain. By amplifying sounds, this stimulation helps the brain’s sound processing region to become more active. This increased activity can improve your ability to hear soft background noise that may otherwise be missed. Hearing other sounds can help you ignore tinnitus.
• Hearing Aids Reduce Communication Stress
Hearing aids are programmed to compensate for your hearing loss. Clear communication reduces the need to strain to hear. Hearing aids help tinnitus by reducing listening stress, which often triggers tinnitus. Having a conversation and hearing other sounds pushes tinnitus into the background.
Stress is a known trigger for tinnitus, read our article on Yoga for tinnitus, recommended yoga exercises for tinnitus relief.
If you have mild hearing loss and do not need amplification, you can use a tinnitus masking device that will produce masking sounds without amplifying the background sound. It is advisable to discuss this with your audiologist before buying a masking device.
How Does Tinnitus Masking Work?
Tinnitus masking or use of masking devices for tinnitus is a method to reduce the perception of tinnitus. The audiologist measures the approximate sensation level or the loudness of tinnitus above the ambient sound.
A hearing aid or a bedside masking device for tinnitus emits a white noise or a suitable tone that is slightly louder than the loudness of tinnitus. The generated sound is calming and less intrusive than the ringing, hissing or thumping tinnitus sound.
Do Hearing Aids Stop Tinnitus?
Tinnitus is a complex issue, hearing aids help tinnitus but do not stop tinnitus, they offer relief. If hearing aids for tinnitus are combined with tinnitus retraining therapy or other tinnitus therapies, the results will be encouraging. To know more, read our article 14 Effective Tinnitus Treatment Options You Need to Know by Dr. Jessica Hinson, Au. D. University of South Alabama.
Can Hearing Aids Make Tinnitus Worse?
Hearing aids cannot make tinnitus worse, in most cases hearing aids help tinnitus. However, there are certain situations where they do not help and can make tinnitus worse.
- Hyperacusis: If you have hyperacusis, then hearing aids may make your tinnitus worse. Hyperacusis is a hearing disorder that makes soft sounds appear very loud and intolerable. The brain amplifies the sound signals more than normally needed resulting in unbearable loud sounds.
- Reactive tinnitus: If it is a case of reactive tinnitus, then hearing aids may not help. Reactive tinnitus is a form of tinnitus that occurs when the loudness and pitch of the tinnitus tone change in response to external sounds. Reactive tinnitus is often associated with hyperacusis.
- Acoustic feedback: If the hearing aid is fitted incorrectly, it may start squealing or whistling; this is known as acoustic feedback. Whistling sounds can aggravate your tinnitus. Hearing aid must be fitted and programmed by a qualified audiologist.
The choice of hearing aid depends on your comfort and lifestyle. Whether you opt for an invisible in-the-ear model or a behind-the-ear type, hearing aids help tinnitus and offer more than just amplified sound. consult your audiologist who can assess your specific needs, recommend the most suitable hearing aid, and guide you throughout the entire process.